If you love jewelry, you probably don’t forget to wear a bracelet to match your style or to show your personality. However, it can become uncomfortable when your bracelet starts hurting your wrist, and you don’t know why and how to fix the problem.
Bracelets hurt your wrist if they are too tight and made of non-breathable material. Tight bracelets can block blood flow, causing pain and swelling. Also, if sweat from your skin gets trapped, it can cause abrasion because of friction. You should wear a breathable and loose bracelet to avoid this.
This article looks closely at the eight most common causes of bracelet-related wrist pain. It also provides solutions for each one, so you can wear your bracelets with peace of mind and without discomfort.
1. Wearing Your Bracelets Tightly

Everyone has their preference of how they like to wear bracelets—some prefer them loose, while others prefer them tight.
However, wearing too-tight bracelets can cause wrist pain. Tight bracelets put unnecessary pressure on your wrist and can cause the muscles and tendons to become inflamed.
Also, wearing tight bracelets can cut off blood circulation to the hand and wrist, leading to tingling, numbness, and nerve damage. In other cases, the bracelet material can scrape your skin, causing rashes and itchiness.
Furthermore, if the bracelet’s material is not breathable, sweat can accumulate and support the growth of bacteria and subsequent infection of the lacerations.
How To Fix
To avoid the discomfort of a tight bracelet, go for a looser fit.
If you don’t like bracelets constantly slipping off or falling off, try a bracelet with a clasp. This way, you can adjust the bracelet to your desired tightness, and there’s no risk of the bracelet falling off and getting lost.
Another solution is to buy bracelets made with stretchy material to easily conform to your wrist size. Also, when purchasing your bracelets, you should try them on to ensure they fit well and are made of breathable material.
2. Allergy to Metallic Bracelet
Most bracelet allergies result from nickel, a metallic substance used in the fashion industry to make less expensive jewelry.
When nickel comes into contact with the skin, it can cause irritation, redness, and itchiness. In severe cases, blistering and permanent scarring can occur. The allergic reaction occurs a few hours after exposure to nickel and can last for two to four weeks on the wrist and sometimes on other body parts.
In most cases, the allergy results from prolonged exposure to nickel bracelets. Once you develop an allergy, your skin will always be sensitive to metals.
How To Fix
The best solution is to avoid nickel-containing bracelets altogether. If you’re unsure whether a bracelet contains nickel, you can always ask the store attendant or do a patch test before you buy it. Or buy a metal testing kit from a dermatologist or pharmacist.
If you still want to wear bracelets, you can try materials less likely to trigger an allergic reaction, such as stainless steel, titanium, and platinum. You can also look for bracelets coated with hypoallergenic materials such as enamel or plastic.
Sadly, there is no cure for metal allergies. However, you can visit a dermatologist to help you manage the condition with nonsteroidal creams or oral antihistamines. They can also guide you in making informed choices while purchasing your bracelets.
3. Wearing Many Bracelets
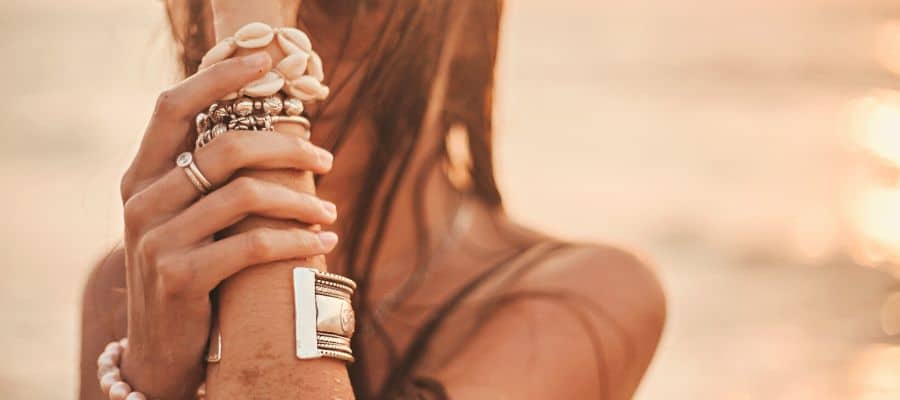

Although there is no standard rule of how many bracelets you should wear on your wrist, putting more than seven bracelets could put too much pressure on your wrist.
When this happens, it is easy to suffer from a wrist sprain. Even if you are not engaging in any physical activity, the constant pressure from the bracelets can cause long-term damage to your wrist.
Also, wearing too many tight and heavy bracelets could make your wrist unbalanced and cut off the blood supply in your hand. This could lead to numbness, swelling, and redness, which could cause discomfort.
In addition, the material of the bracelet also contributes to wrist pain. For example, metallic bracelets are always heavier than beaded ones and wearing too many adds pressure on your wrist.
How To Fix
If you want to use your jewelry to express your sense of style, limiting the number of bracelets you put on your wrist can be inconvenient.
However, for your safety, you should use a maximum of four bracelets on each hand, depending on the size. You should also stack your bracelets well to distribute the weight evenly on your wrist.
If you have a wrist sprain, it is crucial to seek medical attention as soon as possible. A wrist sprain is a severe injury that can take weeks or even months to heal properly. If you do not seek treatment, you could be at risk for permanent damage to your wrist.
4. Arthritis

Arthritis is a disease of the joint that can cause pain and inflammation. It can also affect the tendons and ligaments that attach the bones to the joints. Various factors, including age, injury, and genetics, can cause arthritis.
The most prevalent type of arthritis, osteoarthritis, results from wear and tear of the joints over time. The other is rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease that attacks the joints.
The wrist is a joint made of several bones and connective tissues that allow the bones to glide against each other. Wrist pain is one of the symptoms of arthritis. When you wear bracelets, the pain worsens, and you may experience the following symptoms:
- Red swollen wrist
- Stiffness
- Wrist and hand weakness
- Reduced motion
How To Fix
Unfortunately, there is no cure for arthritis. The solution would be to seek medical attention to manage the pain. If you must wear bracelets, they should be loose and slightly above the wrist on your arm. This reduces pressure on the wrist and allows free movement and circulation of the blood.
5. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
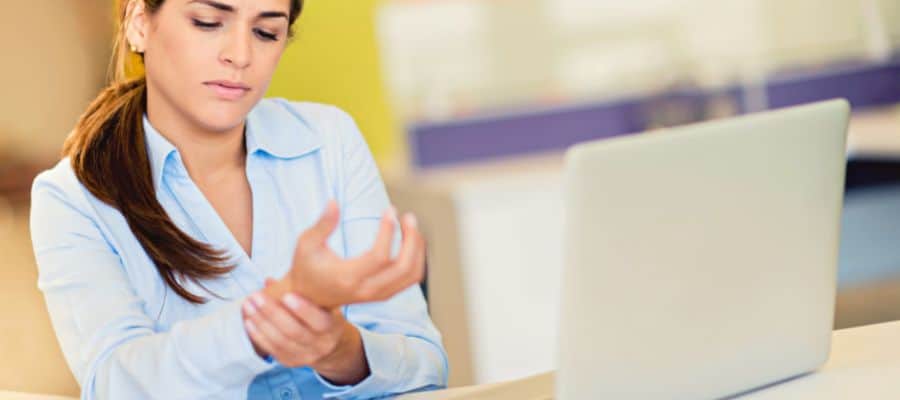

The carpal tunnel is an inch-wide narrow passage in the wrist where the median nerve that provides sensation to the thumb, middle finger, and index finger passes.
The tunnel’s side and the floor consist of carpal bones, while the roof is a strong band of transverse carpal ligament connective tissues. Because its boundaries are rigid, the carpal tunnel does not stretch or increase in size.
Carpal tunnel syndrome results from compression of the median nerve, which moves from the forearm to the hand. But did you know that wearing a bracelet can contribute to this condition?
Here’s how it works: When you wear a bracelet, it puts pressure on the soft tissue and muscles in your wrist. This pressure compresses the nerve, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain in your wrist and hand.
The risk of carpal tunnel syndrome can increase if you wear tight bracelets while working.
How To Fix
If you are experiencing symptoms similar to carpal tunnel syndrome, you should refrain from wearing bracelets because the condition could worsen with time. You should also visit a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment. The common methods of treatment include:
- Neurosurgical treatment. If your symptoms are mild, the doctor will recommend non-surgical treatment, including splinting, steroid injection, nerve gliding exercise, and a change of activities.
- Surgical treatment. Where the condition has caused wasting of your wrist muscles, you might undergo surgery to prevent irreversible damage.
6. Wearing Bracelets with Rough Edges

When it comes to style, fashionistas will design anything without paying much attention to your safety. Some bracelets come with pointy and rough edges that prick your wrist despite being loose. Wearing such a bracelet for a long time can perforate your skin and cause swelling and inflammation.
Also, most bracelets with rough edges are metallic, meaning they are non-breathable. In the presence of heat, your sweat gets trapped between your skin and the bracelet, causing itchiness.
How To Fix
If bracelets with rough edges are harming your skin, the best solution is to replace them with other models with smooth edges.
But it can be painful not to wear your bracelet if you paid a hefty amount for it. If you still want to wear it, you can try the following:
- Return it to the seller. If the bracelet is new and you have not altered it, you can return it to the seller for a replacement and fit in the replacement to avoid repeating the same mistake.
- File the rough edges. You can try smoothing the edges using a file. This method is risky as you might damage the bracelet. The alternative would be to look for a professional jeweler to smooth it for you. Remember, if you alter the bracelet, you cannot return it to the seller if it has a warranty.
- Attach a soft adhesive. On the inner surface of the bracelet, where the edges touch the skin, you can attach a soft, breathable material to act as a barrier. It might not be a long-term solution, but it will prevent your wrist from harm.
7. Wrist Tendinitis
Wrist tendinitis is the inflammation of the tendons in your wrist. Though there are six tendons on your wrist, it mainly affects the tendon in the carpal tunnel.
The symptoms include pain, swelling, and tenderness in the wrist area. The condition can result from wrist overuse, such as repetitive motions when typing or using a mouse. Also, it can result from an injury or direct blow to the wrist.
Wearing bracelets while suffering from wrist tendinitis elevates the pain because it compresses the nerves that are already swollen. The condition occurs mostly in people who do strenuous activities using the wrist or new mothers who spend hours holding a baby.
How To Fix
Wrist tendinitis is a common condition that is curable using the following methods:
- RICE method. This at-home treatment involves resting, icing, compressing, and elevating your wrist. You should ice the wrist for 20 minutes several times a day. You should also refrain from pushing through the pain by lifting heavy objects or rotating the wrist to allow the tendons to heal.
- Medication. You can take ibuprofen or aspirin to reduce pain and inflammation. If the pain persists, you should see a doctor for a corticosteroid injection or surgery.
- Splinting. This involves using a splint or a supportive device to stabilize your wrist.
8. Repetitive Stress Injuries
If you’re constantly wearing bracelets, whether for fashion or function, you might be at risk of developing a repetitive stress injury (RSI).
An RSI is a gradual buildup of muscle, tendons, and nerve injury caused by repeating the same motion over and over. And while it might not seem like wearing a bracelet would fall into this category, if you wear tight and heavy bracelets day in and day out and work using your hands, it qualifies.
The most common type of RSI from wearing bracelets is de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis, which is a condition that causes pain, tenderness, tingling, and numbness in the wrist and hand.
How To Fix
If you have de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis, you can do the following:
- Reduce pressure on your wrist. You should take a break from wearing bracelets as much as possible. If you have to wear them, ensure they’re not too tight or constricting.
- Apply ice or heat on the wrist. You can apply an ice pack to your wrist for 20 minutes to help reduce the swelling or massage the affected area with a hot towel.
- Take medication. You can take naproxen or ibuprofen to help with the pain and inflammation. If the pain persists, you should get a steroid injection.
- Avoid repetitive movements. If you work with your hands, take breaks often and vary your tasks throughout the day to relax the wrist muscles. And when wearing bracelets, try to choose lighter styles that aren’t too tight.
Final Thoughts
It’s not unusual for bracelets to hurt your wrist. However, you should take the following precautions:
- Wear smooth, loose, or stretchy bracelets to avoid compressing the wrist.
- Don’t wear more than four bracelets to reduce pressure on the wrist.
- Ensure even distribution of weight on your wrist.
Sometimes, wearing bracelets may elevate underlying health conditions, and you might need medical treatment.
If you found this article useful, make sure you save this pin below to your Jewelry board.


